AiCEF - An AI-assisted cyber exercise content generation framework using named entity recognition
AiCEF is a tool implementing the accompanying framework [1] in order to harness the intelligence that is available from online resources, as well as threat groups' activities, arsenal (eg. MITRE), to create relevant and timely cybersecurity exercise content. This way, we abstract the events from the reports in a machine-readable form. The produced graphs can be infused with additional intelligence, e.g. the threat actor profile from MITRE, also mapped in our ontology. While this may fill gaps that would be missing from a report, one can also manipulate the graph to create custom and unique models. Finally, we exploit transformer-based language models like GPT to convert the graph into text that can serve as the scenario of a cybersecurity exercise. We have tested and validated AiCEF with a group of experts in cybersecurity exercises, and the results clearly show that AiCEF significantly augments the capabilities in creating timely and relevant cybersecurity exercises in terms of both quality and time.
We used Python to create a machine-learning-powered Exercise Generation Framework and developed a set of tools to perform a set of individual tasks which would help an exercise planner (EP) to create a timely and targeted Cybersecurity Exercise Scenario, regardless of her experience.
Problems an Exercise Planner faces:
- Constant table-top research to have fresh content
- Realistic CSE scenario creation can be difficult and time-consuming
- Meeting objectives but also keeping it appealing for the target audience
- Is the relevance and timeliness aspects considered?
- Can all the above be automated?
Our Main Objective: Build an AI powered tool that can generate relevant and up-to-date Cyber Exercise Content in a few steps with little technical expertise from the user.
Release Roadmap
The updated project, AiCEF v.2.0 is planned to be publicly released by the end of 2023, pending heavy code review and functionality updates. Submodules with reduced functinality will start being release by early June 2023. Thank you for your patience.
Installation
The most convenient way to install AiCEF is by using the docker-compose command. For production deployment, we advise you deploy MySQL manually in a dedicated environment and then to start the other components using Docker.
First, make sure you have docker-compose installed in your environment:
Linux:
$ sudo apt-get install docker-composeThen, clone the repository:
$ git clone https://github.com/grazvan/AiCEF/docker.git /<choose-a-path>/AiCEF-docker
$ cd /<choose-a-path>/AiCEF-dockerConfigure the environment settings
Import the MySQL file in your
$ mysql -u <your_username> –-password=<your_password> AiCEF_db < AiCEF_db.sql Before running the docker-compose command, settings must be configured. Copy the sample settings file and change it accordingly to your needs.
$ cp .env.sample .envRun AiCEF
Note: Make sure you have an OpenAI API key available. Load the environment setttings (including your MySQL connection details):
set -a ; source .envFinally, run docker-compose in detached (-d) mode:
$ sudo docker-compose up -dUsage
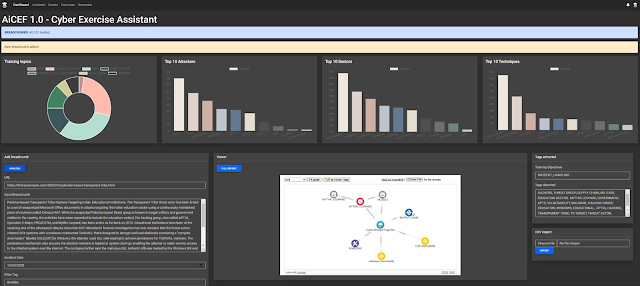
A common usage flow consists of generating a Trend Report to analyze patterns over time, parsing relevant articles and converting them into Incident Breadcrumbs using MLTP module and storing them in a knowledge database called KDb. Incidents are then generated using IncGen component and can be enhanced using the Graph Enhancer module to simulate known APT activity. The incidents come with injects that can be edited on the fly. The CSE scenario is then created using CEGen, which defines various attributes like CSE name, number of Events, and Incidents. MLCESO is a crucial step in the methodology where dedicated ML models are trained to extract information from the collected articles with over 80% accuracy. The Incident Generation & Enhancer (IncGen) workflow can be automated, generating a variety of incidents based on filtering parameters and the existing database. The knowledge database (KDB) consists of almost 3000 articles classified into six categories that can be augmented using APT Enhancer by using the activity of known APT groups from MITRE or manually.
Find below some sample usage screenshots:
Features
- An AI-powered Cyber Exercise Generation Framework
- Developed in Python & EEL
- Open source library Stixview
- Stores data in MYSQL
- API to Text Synthesis Models (ex. GPT-3.5)
- Can create incidents based on TTPs of 125 known APT actors
- Models Cyber Exercise Content in machine readable STIX2.1 [2] (.json) and human readable format (.pdf)
Authors
AiCEF is a product designed and developed by Alex Zacharis, Razvan Gavrila and Constantinos Patsakis.
References
[1] https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10207-023-00693-z
[2] https://oasis-open.github.io/cti-documentation/stix/intro.html
Contributing
Contributions are welcome! If you'd like to contribute to AiCEF v2.0, please follow these steps:
- Fork this repository
- Create a new branch (
git checkout -b feature/your-branch-name) - Make your changes and commit them (
git commit -m 'Add some feature') - Push to the branch (
git push origin feature/your-branch-name) - Open a new pull request
License
AiCEF is licensed under Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) license. See for more information.
Under the following terms:
Attribution — You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use. NonCommercial — You may not use the material for commercial purposes. No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits.
 Reviewed by Zion3R
on
8:30 AM
Rating:
Reviewed by Zion3R
on
8:30 AM
Rating: